The case for using this access is inside a UVM Testbench, where the test would generate some randomization on the data and need to access the instantiated module (let say model in this case) in the top.
Overview
One naive solution in my case is using UVM’s configuration database (uvm_config_db) to pass down the model handle from the top to the test component. The above solution won’t work since the module cannot be passed inside uvm_config_db This is where the following solution should be useful.
The workaround
For the workaround demonstration, a simple UVM testbench generated with EasierUVM will be used.
Overview of the testbench
// Update the graph later with the model’s module
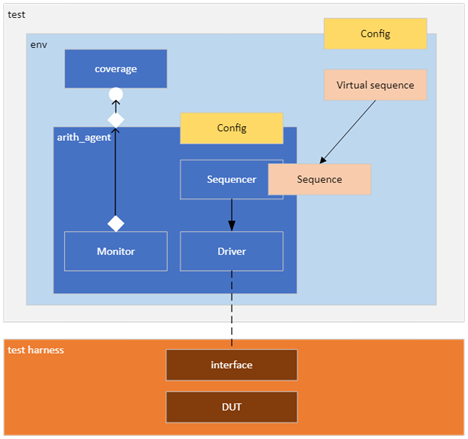
Implementation
The DUT in this case is a simple ALU’s adder
module adder (
input logic [7:0] A,
input logic [7:0] B,
output logic [8:0] F
);
always_comb
F <= A+B;
endmoduleThe module wanted to be accessed from the test is the input generator (this is for demonstration purpose only, for normal UVM testbench this should be implemented as UVM driver-driver BFM pair)
module input_model (
input logic clk,
output logic [7:0] A,
output logic [7:0] B
);
logic [7:0] input_pool[*];
int current_index = 0;
int rand_index = 0;
reg [7:0] reg_A;
reg [7:0] reg_B;
// Function to be called for adding randomized input
function void insert_input(logic[7:0] value);
input_pool[current_index++] = value;
$display("INPUT MODEL: Currently inserting: 0x%8x at index %d", value, current_index-1);
endfunction : insert_input
always @(posedge clk) begin
assert ( randomize(rand_index) with { rand_index inside {[0:current_index-1]}; }) else
begin
$display("why the fuck can it not randomize properly?");
end
$display("Current rand_index: %d", rand_index);
$display("Current current_index: %d", current_index);
reg_A <= input_pool[rand_index];
reg_B <= input_pool[rand_index];
end
assign A = reg_A;
assign B = reg_B;
endmodule : input_modelThe package containing the virtual class extending uvm_object → This will be used in other testbench’s class components
package backdoor_access_pkg;
import uvm_pkg::*;
virtual class input_model_backdoor extends uvm_pkg::uvm_object;
function new(string name="input_model_backdoor");
super.new(name);
endfunction
pure virtual function void insert_input(logic [7:0] value);
endclass : input_model_backdoor
endpackage : backdoor_access_pkgThe wrapper class for the module that extends and implement all the virtual methods of the created virtual class
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
import uvm_pkg::*;
import backdoor_access_pkg::*;
class backdoor_im extends input_model_backdoor;
function new(string name="backdoor_im");
super.new(name);
endfunction : new
function void insert(logic[7:0] value);
top_tb.th.model.insert_input(value);
endfunction : insert
endclass : backdoor_im
initial begin
backdoor_im backdoor_im_i;
backdoor_im_i = new();
uvm_config_db #(uvm_object)::set(uvm_root::get(), "*", "IM_BACKDOOR_ACCESS", backdoor_im_i);
end- Adding the handle to the
uvm_config_dbunderuvm_root::get()as the parent,*as the scope, key string and the handle itself: - Instantiating it in the
top.sv, (top_tb.svin this example)
module top_tb;
timeunit 1ns;
timeprecision 1ps;
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
import uvm_pkg::*;
import top_test_pkg::*;
import top_pkg::top_config;
// Configuration object for top-level environment
top_config top_env_config;
// Test harness
top_th th();
`include "backdoor_input_model.sv"
initial
begin
// Create and populate top-level configuration object
top_env_config = new("top_env_config");
if ( !top_env_config.randomize() )
`uvm_error("top_tb", "Failed to randomize top-level configuration object" )
top_env_config.arith_vif = th.arith_if_0;
top_env_config.is_active_arith = UVM_ACTIVE;
top_env_config.checks_enable_arith = 1;
top_env_config.coverage_enable_arith = 1;
uvm_config_db #(top_config)::set(null, "uvm_test_top", "config", top_env_config);
uvm_config_db #(top_config)::set(null, "uvm_test_top.m_env", "config", top_env_config);
run_test();
end
endmoduleIncluding the packages in the environment (in this case in the agent’s package)
package arith_pkg;
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
import uvm_pkg::*;
import backdoor_access_pkg::*;
`include "arith_trans.sv"
`include "arith_config.sv"
`include "arith_driver.sv"
`include "arith_monitor.sv"
`include "arith_sequencer.sv"
`include "arith_coverage.sv"
`include "arith_agent.sv"
`include "arith_seq_lib.sv"
endpackage : arith_pkgAnd the remaining is to access the module from the test using the virtual class, by fetching the handle from the uvm_config_db as an uvm_object and cast it to the correct type of the virtual class
`ifndef TOP_TEST_SV
`define TOP_TEST_SV
// You can insert code here by setting test_inc_before_class in file common.tpl
class top_test extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(top_test)
// Change made here
top_env m_env;
logic [7:0] rand_input = 0;
// end : Change made here
backdoor_access_pkg::input_model_backdoor backdoor_im_i;
uvm_object backdoor_object_i;
extern function new(string name, uvm_component parent);
extern function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
extern task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
endclass : top_test
function top_test::new(string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction : new
function void top_test::build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
m_env = top_env::type_id::create("m_env", this);
// Fetching the handle from the uvm_config_db and cast it to the correct type
if(!uvm_config_db#(uvm_object)::get(uvm_root::get(), "", "IM_BACKDOOR_ACCESS", backdoor_object_i))
begin
`uvm_fatal("TEST","Failed to get input model backdoor access object")
end
assert($cast(backdoor_im_i, backdoor_object_i)) else begin
`uvm_fatal("ASSERT", "Dynamic casting backdoor_im_instance failed!")
end
endfunction : build_phase
task top_test::run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
$display("Went in the run_phase of the test!");
#10;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) begin
assert (randomize(rand_input));
backdoor_im_i.insert(rand_input);
end
#1000;
endtask
`endif // TOP_TEST_SVAlso remember to compile the .sv file and packages properly. The compiling sequence should be included in the compile_questa.do script.
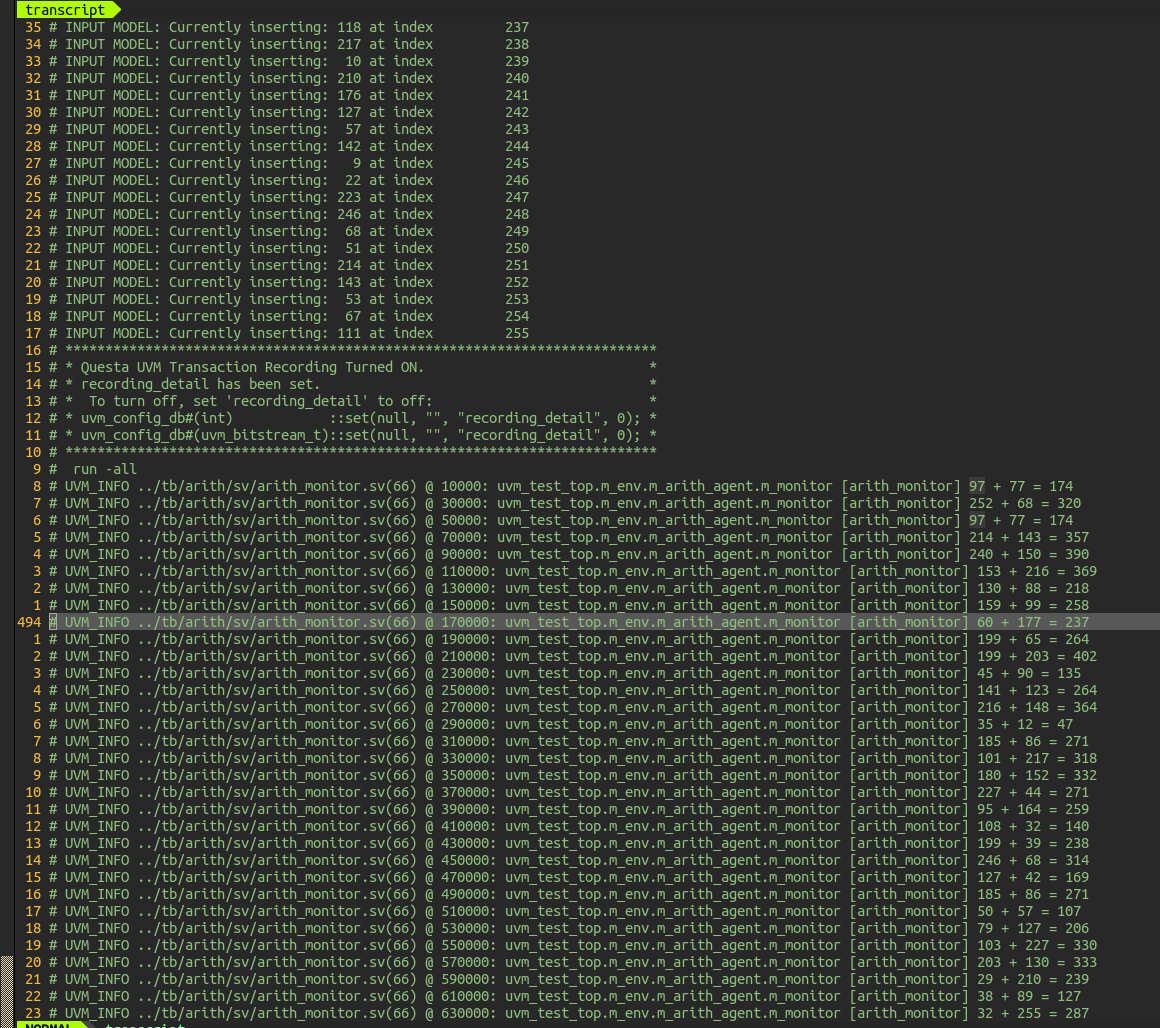
The result when running the simulation
The result when dumping signals, by adding some signals on top_th.sv and a little addition on top_tb.sv file
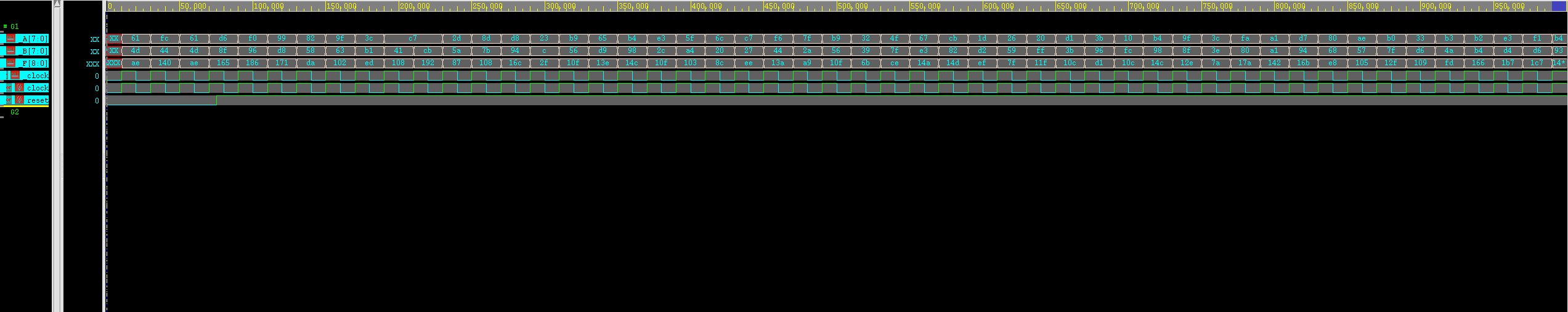
This result concludes the ability to manipulate the module that is instantiated on the top from a test component in UVM testbench
Full testbench can be found here.
Summary
Create a virtual class extending
uvm_object(for exampleVC)Create a wrapper class for the module that extends and implement all the virtual methods of the created virtual class
- Instantiating it in the
top.sv - Adding the handle to the
uvm_config_dbunderuvm_root::get()as the parent,*as the scope, key string and the handle itself:
system-veriloguvm_config_db #(uvm_object)::set( uvm_root::get(), "*", "<KEY>", <wrapper_handle> );This will ensure the scope of the statement used to call the
top's instantiated module.Meaning the statement
top.<module_name>.<method_name>()should be valid.- Instantiating it in the
The virtual class
VCmentioned above will be used for the lower level component in the environment hierarchy for accessing the top instantiated module’s methods.
