Register-Based Testing
Contents are extracted from the Advanced UVM sessions by Verification Academy.
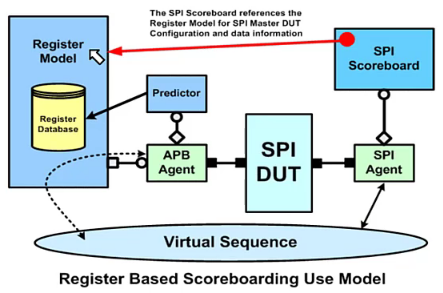
Register-based analysis components
The register model mirror value is used by analysis components
- Scoreboards to check current DUT configuration
- Where this may affect the checking algorithm
- Functional coverage monitors
- What is the configuration at a triggered sample?
Analysis components access physical registers passively (using the backdoor accesses):
- No ability to drive the bus
- Backdoor
read()orpeek()accesses
They look up the register model values directly
spi_rm.ctrl.get_mirrored_value(data);spi_rm.ctrl.valueorspi_rm.ctrl.get(data);
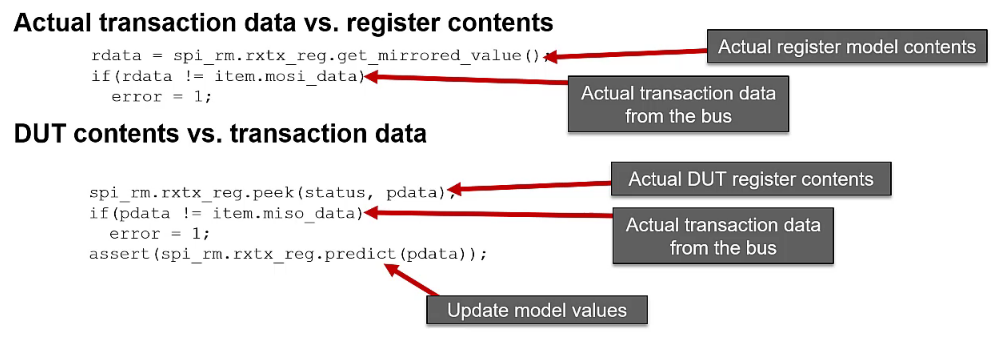
Register Scoreboard guidelines
Scoreboard needs a handle to the register model
Scoreboard accesses register values from model
Scoreboard checks DUT register contents
- Compare observed data vs. register model contents
- Compare DUT contents vs. expected
- via peek access to the DUT
Scoreboard checking
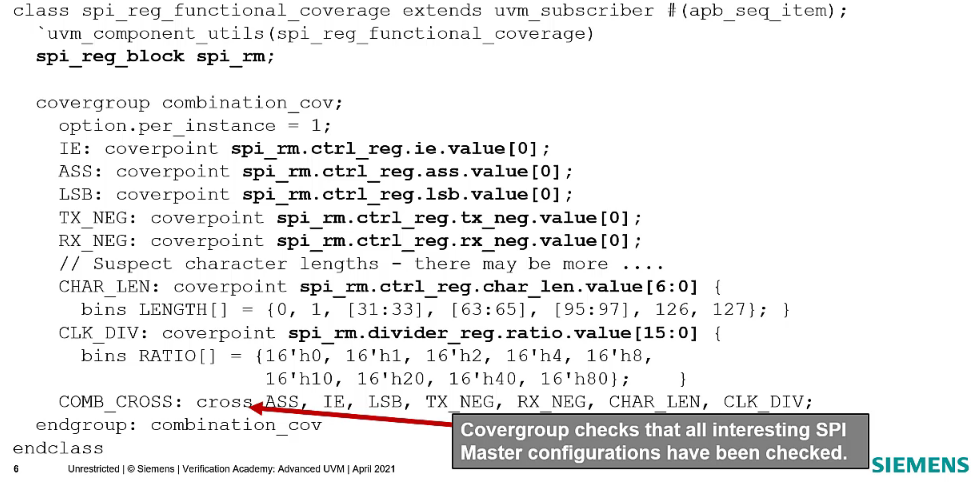
Functional coverage monitors
The register model has built-in functional coverage

A custom functional coverage monitor can be defined to sample based on significant events
- Interrupts
- Writes to certain trigger registers
Register Assistant generates ‘intelligent’ register access covergroup
- Included in the register package code
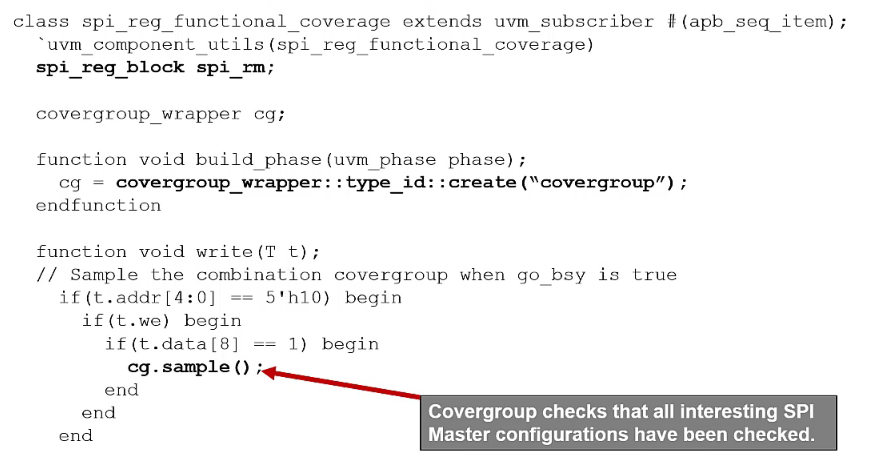
Functional coverage monitor example

Coding guideline
Allow the ability to override
covergroupwhen necessary (uvm_objectis overridden)
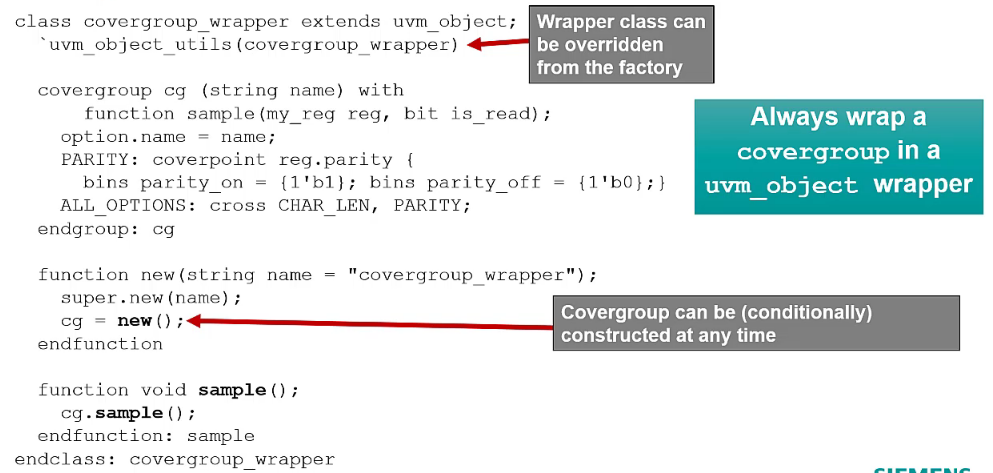
Monitor with Wrapped covergroup
Modeling memory
The register model provides access to memory region
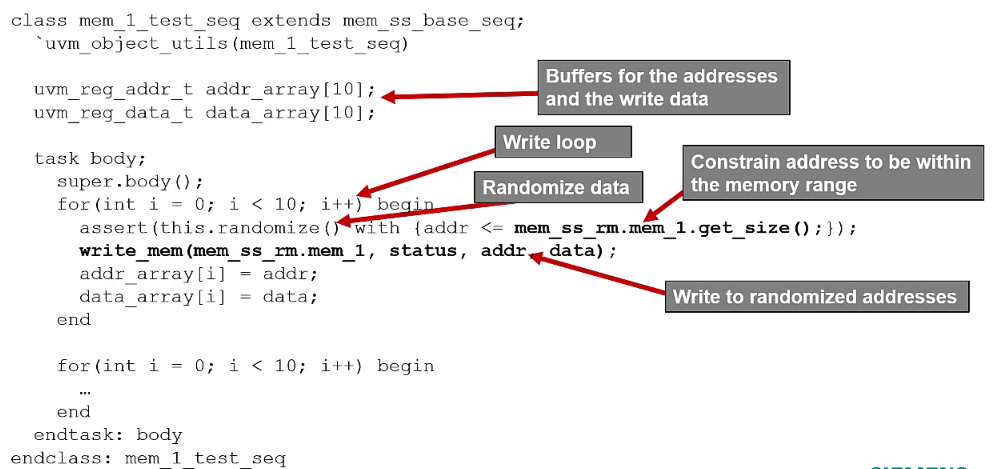
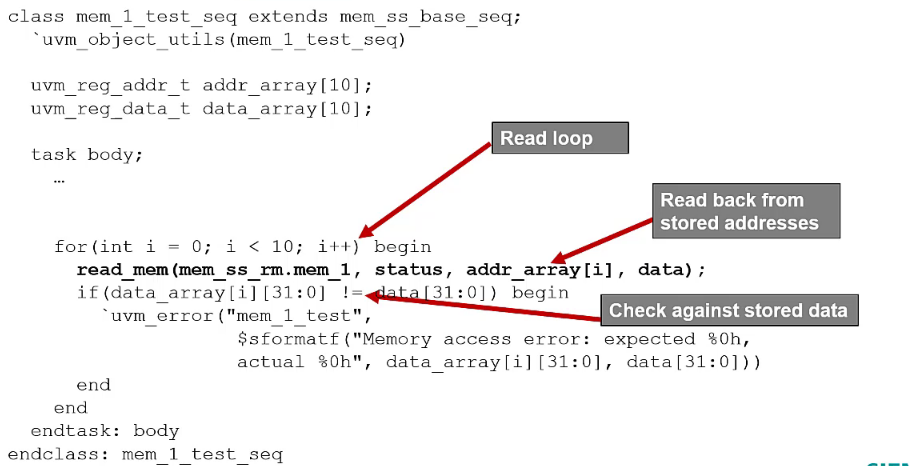
mem.read()/mem.write()to location x in memory yThe memory location address offset is calculated
system-verilogmem.read(status, offset_addr, data, ...); mem.write(status, offset_addr, data, ...);
The model does not shadow memory regions
- DUT memories are usually modelled separately
- Maintaining a memory shadow is expensive
- No
set()/get()functions available
Memory accesses can support bursts
mem.burst_read()mem.burst_write()
Example memory based sequence
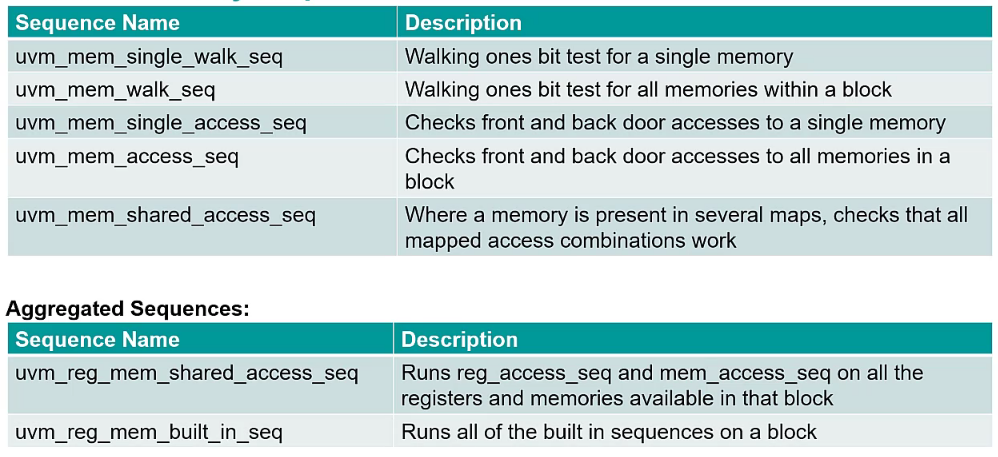
Built-in Memory sequences
Register Summary
Register block contains
- Register model
- Fields
- Address Map
- Sub-blocks
Register analysis components have register block pointer
- Access via
get()or backdoor read/peek - Use
model.reg.valuedirectly
Wrap covergroups to increase flexibility
Use built-in test sequences for sanity checking
- Registers and memories