The Proper Care and Feeding of Sequences
Contents are extracted from the Advanced UVM sessions by Verification Academy.
Review
The sequence is always known to have a name when being instantiated - Good convention
It is possible to reuse a initiated sequence object every iteration if there is guarantee on how the sequence data changed each iteration
TLM passing the handle of the sequence, must guarantee if the driver or any other component having the handle either make a copy of the handle or finish processing handle
When
start_itemreturns → Driver is ready to accept the transaction
finish_itemis called to send the transaction after the late randomization
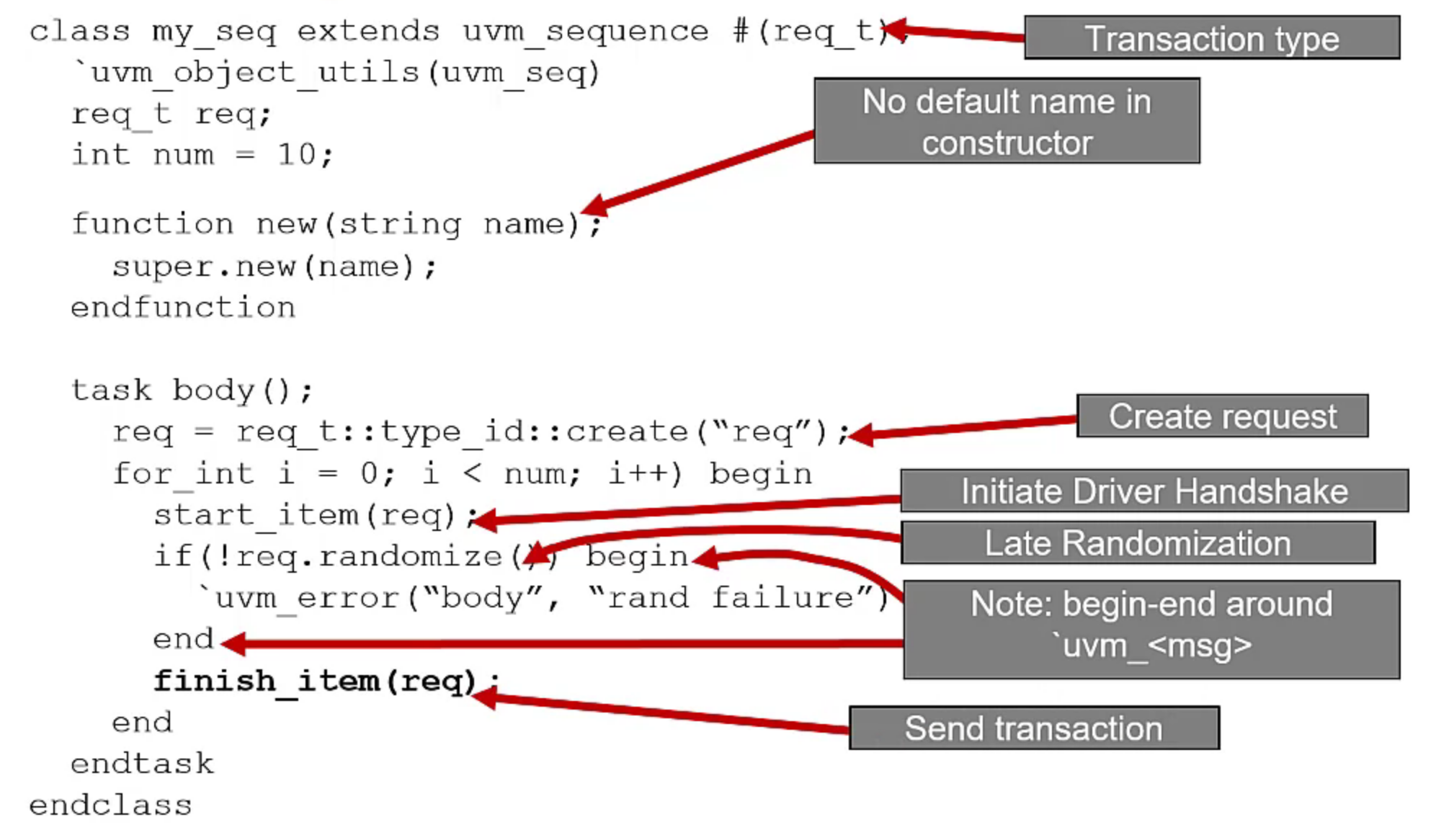
Sequencer is recommended to be declared as a class with factory registration
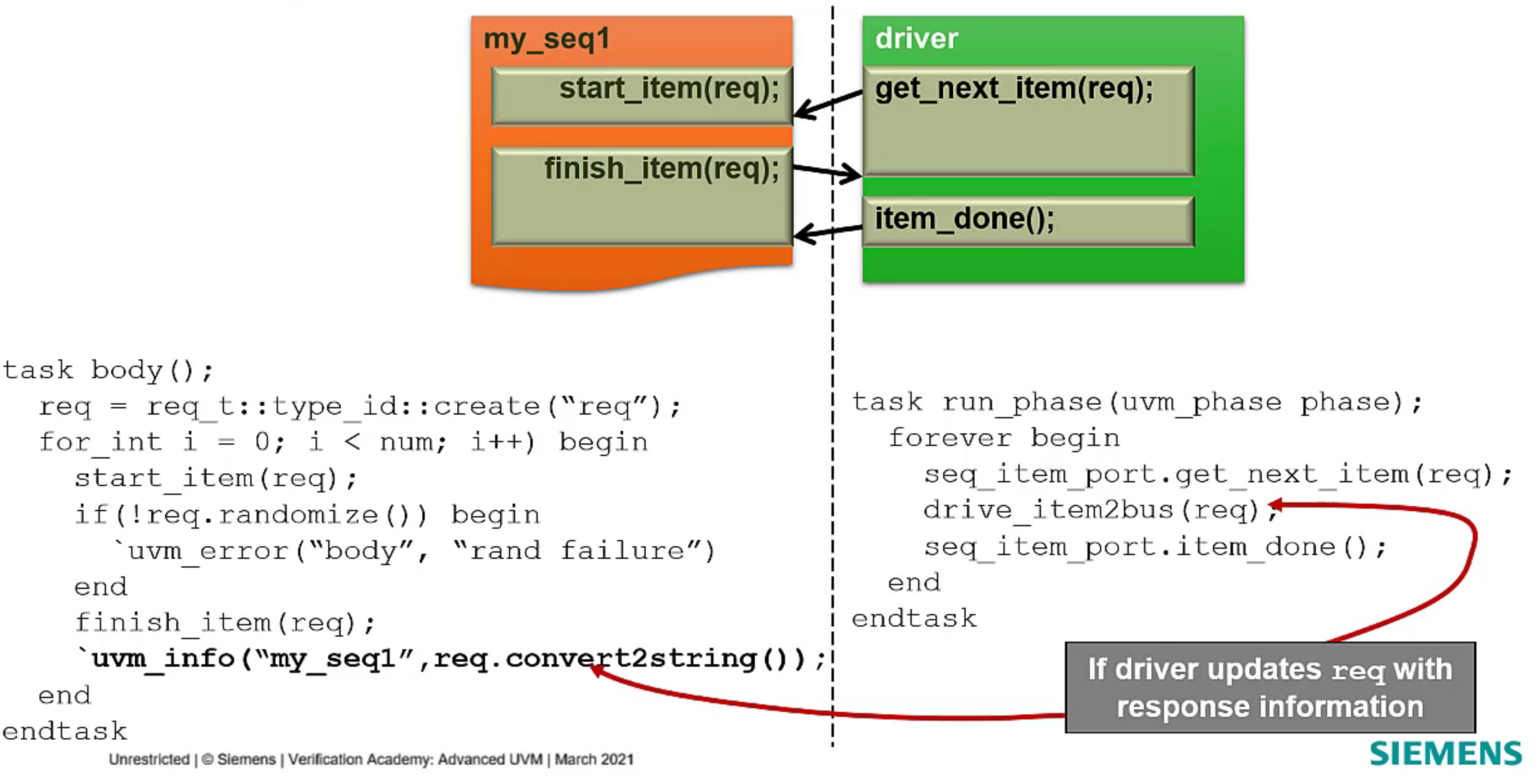
Sequencer/Driver handshake
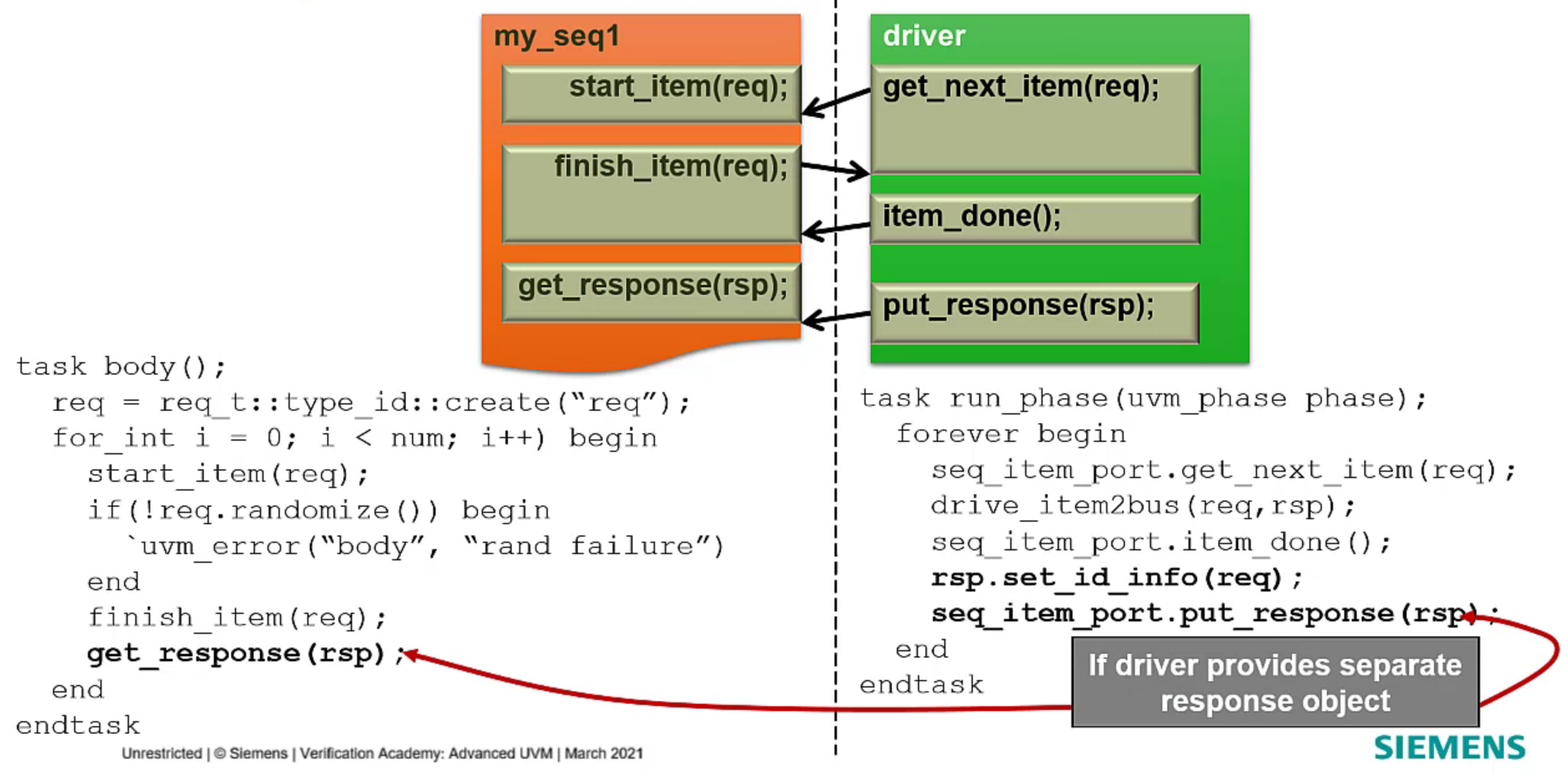
- Cases where the driver also receive the response and sequence will be waiting for it:
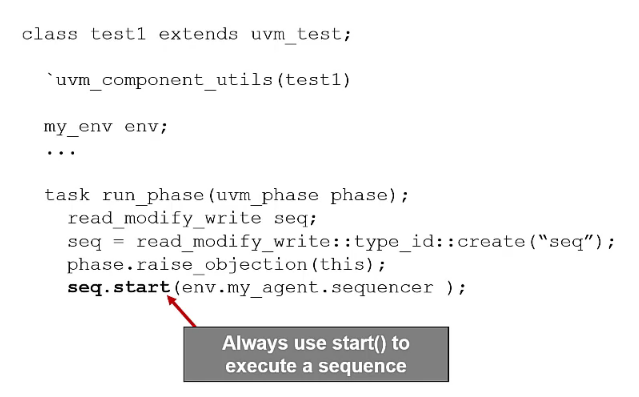
Sequence start
Starting sequence from the test
Sequence can also be started from the environment also
Behave like background/default sequence also

Arbitration and Responses in the Sequencer
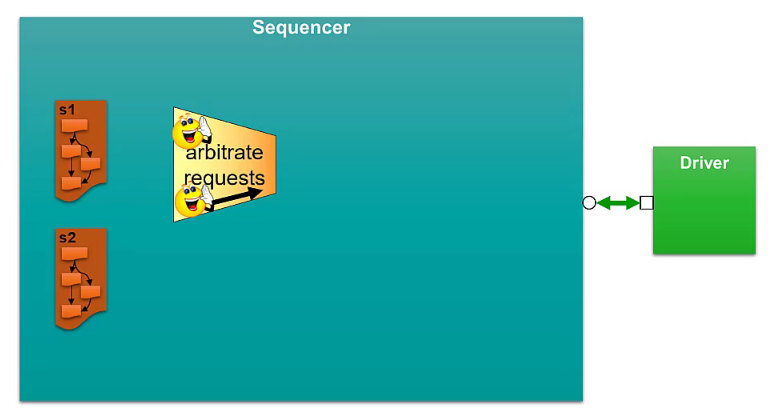
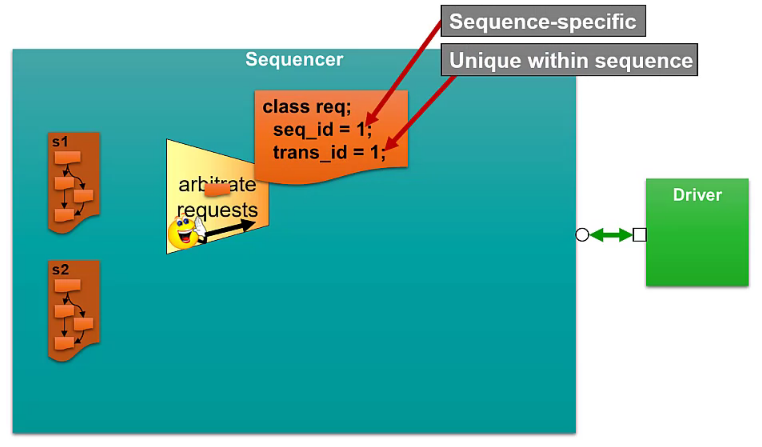
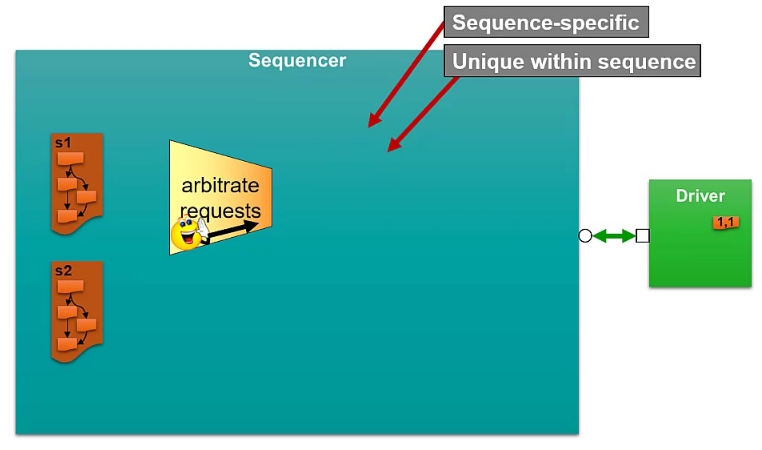
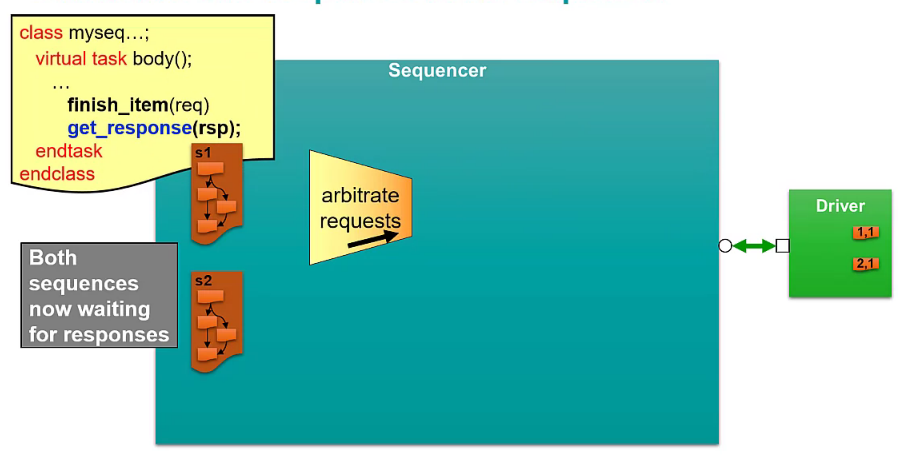
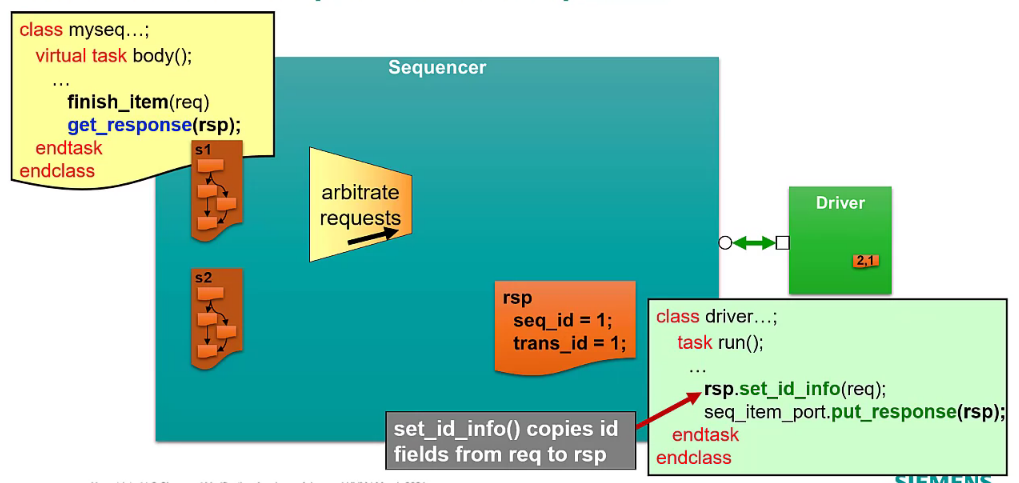
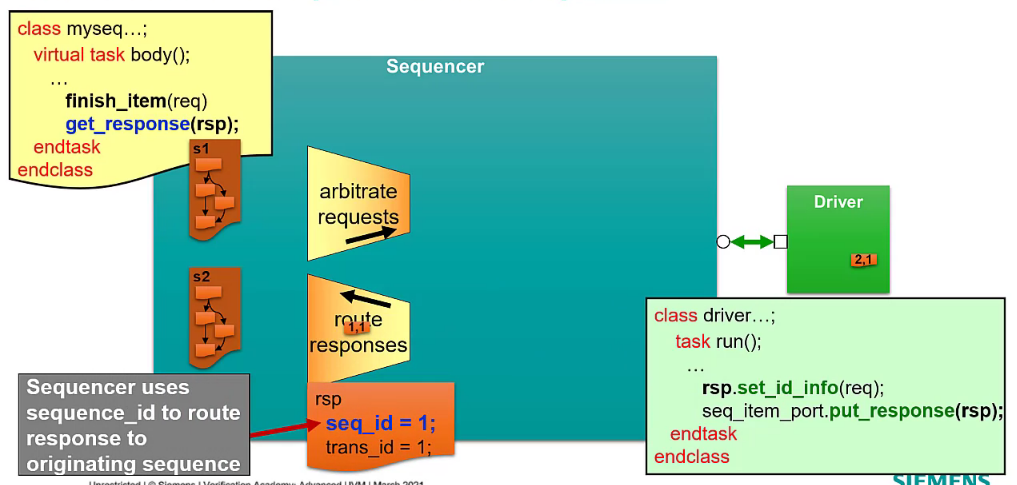
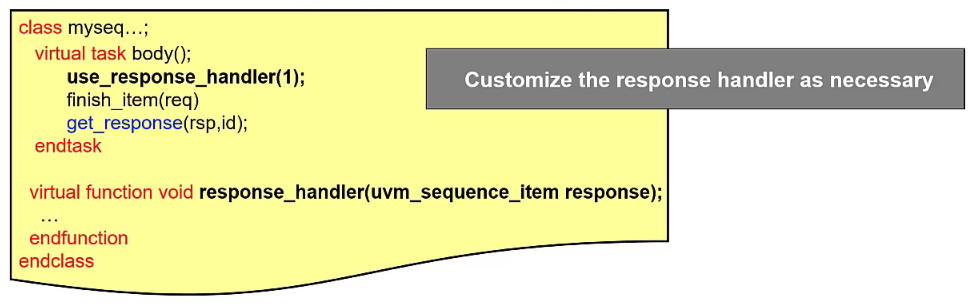
Optional: additional response id field to indicate which transaction to be received on the sequence
Get response call will not return until the transaction with matching transaction id is returned
Typically used in sequences with
fork..joinon multiple threads running concurrentlyResponse item FIFO can only hold 8 items at a time

Sequential sequences
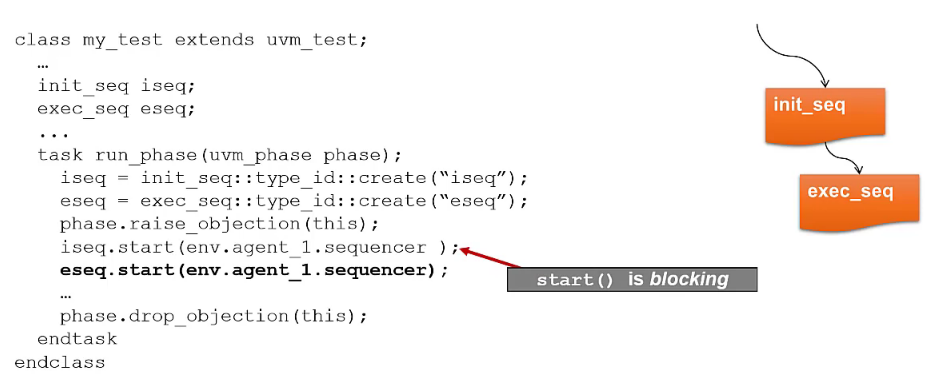
start()is blocking so theexec_seqwon’t start until theinit_seqfinish executing
Parallel sequences
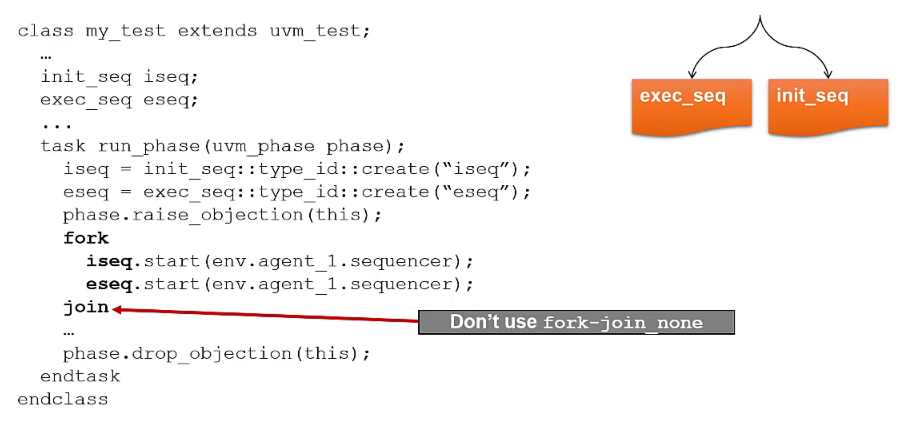
Have to implement additional checking logic to indicate the end of the execution when using
fork-join_noneto explicitly drop the objection
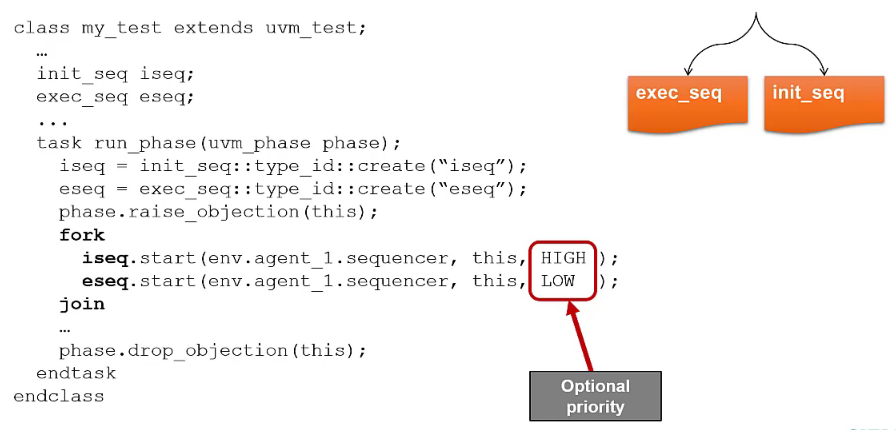
Hierarchical sequences

thisargument specify the parent sequence of the currently starting sequence

Pipelined Driver
Start another sequence before the finish of previous sequence
Involved calling the task multiple time in
fork..joinblock

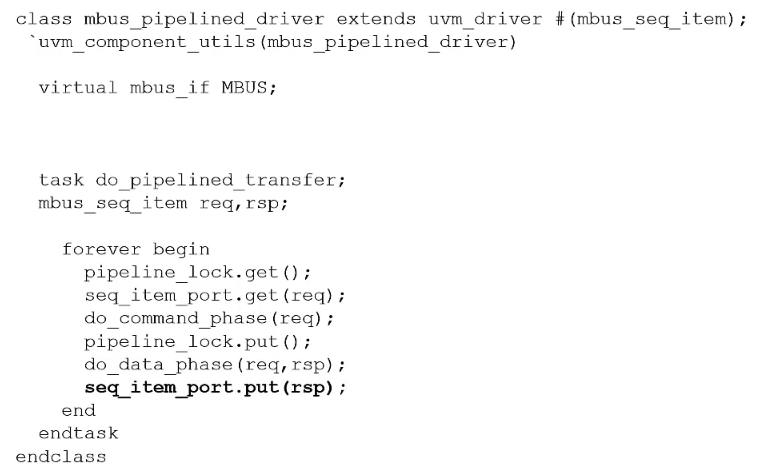
pipeline_lock.get()andpipeline_lock.put()are the semaphore and the its methods to control the resources
getclaim the lock
putrelease the lock
Summary
Make sure to parameterize sequence/sequencer/driver with the same request and response types
Start sequences using seq.start(sequencer)
Use seq_item_port.get_next_item/item_done in the driver
- Use
try_next_item/item_doneif driver must perform idle cycles - Use
get/putfor pipelined drivers
Use API from test or parent sequence to configure sequences
Sequence and Driver must agree on response path, if any